- Graphites
- Isostatic Graphite
- Molded Graphite
- Extruded Graphite
- Vibration Graphite
- Mechanical Carbon Graphite
- Graphite Box for Anode Material
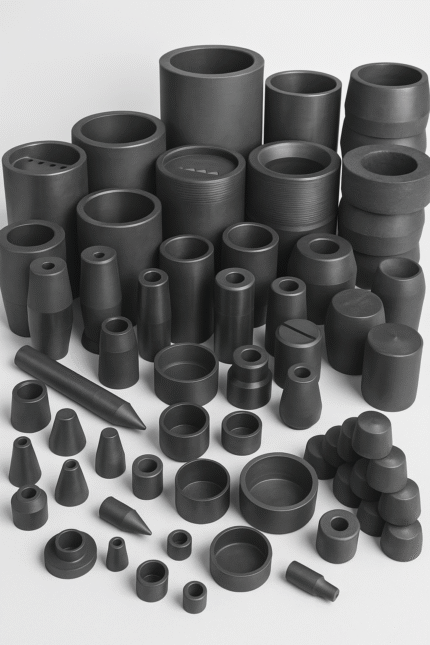
- CNC Machining Graphite Parts
- CNC Machining Graphite Parts
- Graphite Electrode
- Graphite Bipolar Plate
- Carbon Brush/Electric Brush
- High-Purity Graphite Powder for Lithium-Ion Battery Applications
- Graphite Hot Zone for PV
- Calcined Petroleum Coke
- Graphite Products for Glass Industry
- Graphite Crucible
- Graphite Pipe
- Graphite Rod/Block/Plate
- Expanded Graphite Powder – High Conductivity Grade BZ-20
- C-C Composites
- 2D
- 2D Carbon-Carbon Composite Sheets and Plates
- 2.5D Carbon-Carbon Composite Materials
- 3D Carbon-Carbon Composite Materials
- 4D / 5D Carbon-Carbon Composite Materials
- High-Density Carbon-Carbon Composite Materials
- Carbon-Carbon Composite Aircraft Brake Discs
- Carbon-Carbon Composite Heaters & Heating Elements
- Carbon-Carbon Composite Insulation Barrels & Blankets
- Carbon-Carbon Composite Moulds
- Carbon-Carbon Composite Screws & Studs
- Carbon Carbon Composite Crucible
- Carbon Carbon Composite U & L Profiles
- Carbon Carbon Composite Blocks
- Carbon Carbon Composite Racing Brake Discs and Pads
- Carbon Carbon Composite Rods, Tubes, and Pipes
- Carbon Composite Bolts and Nuts
- Carbon Ceramic Composite Materials and Precision Parts
- Pyrolytic Graphite
- Carbon Felt / Graphite Felt
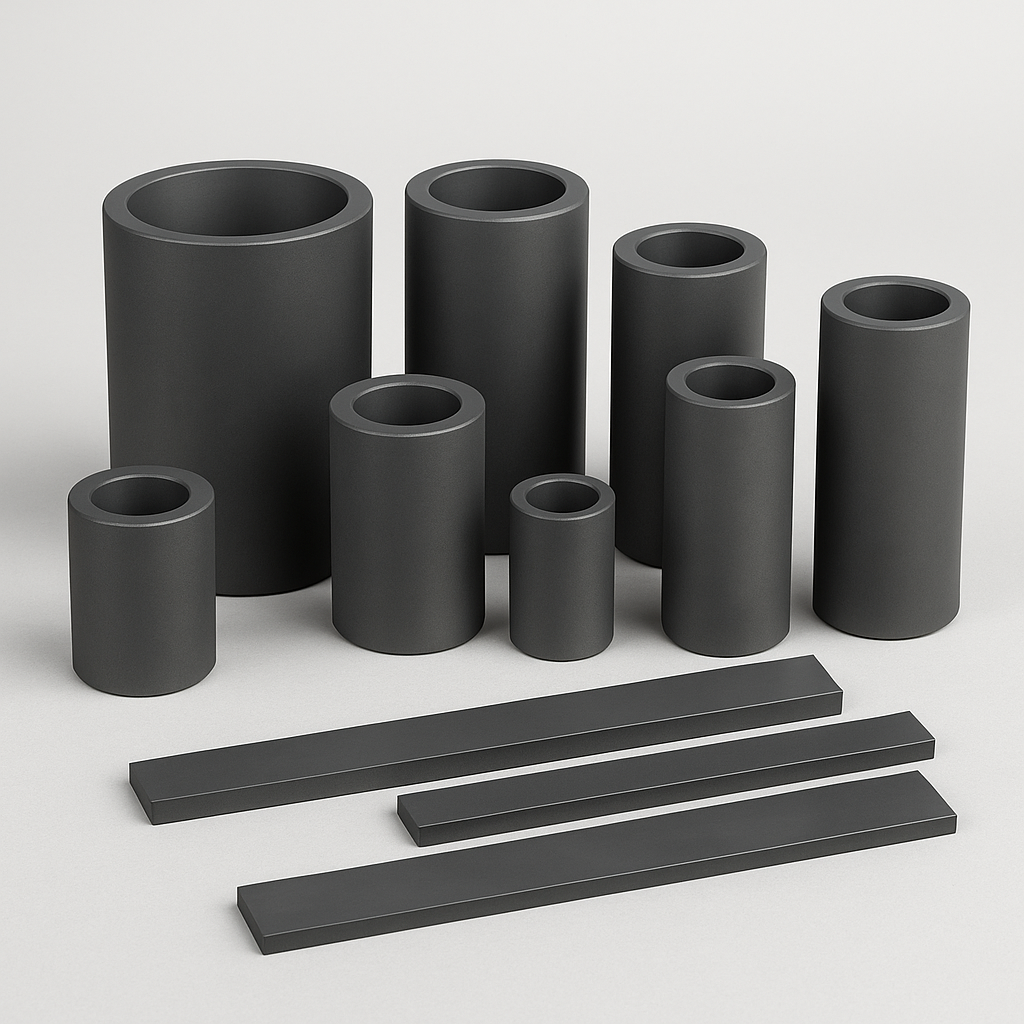
Mechanical Carbon Graphite
At BZNCarbon, we produce and supply impregnated mechanical carbon graphite materials with stable quality and custom configurations for demanding industrial applications. These composites are formulated by impregnating graphite with various agents such as resin, copper, antimony, and silver, resulting in enhanced performance in conductivity, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance.
Category: Graphites
Tag: Mechanical Carbon Graphite
Description
What is Impregnated Graphite?
Impregnated graphite is a composite material formed by filling pores of base graphite with impregnating substances (resin or metals), then solidifying through high-temperature treatment. This process enhances strength, sealing ability, conductivity, and chemical durability.
Main Types of Mechanical Carbon Graphite
Resin Impregnated Graphite
High density (up to 2.0–2.5 g/cm³)
Excellent corrosion resistance
Ideal for chemical environments, seals, and bearings
Max temperature resistance: ~200°C
Grades: M106H, M120H, M106K, M120K, M254K
Copper Impregnated Graphite
Combines the mechanical strength of copper and thermal conductivity of graphite
Used in rolling equipment, metallurgy, turbines, molding machines
Grades: M106P, M120P, M254P
Antimony Impregnated Graphite
Superior lubrication and wear resistance under extreme conditions
Operating range: −253°C to +500°C
Works under high RPM (20,000), high pressure (10 MPa)
Grades: M106D, M120D, M254D
Silver and Other Metal Impregnated Graphite
Enhanced conductivity and durability
Used in specialized high-tech fields
Key Features
Self-lubricating with or without oil
Excellent resistance to high temperatures, corrosion, and pressure
High electrical conductivity and dimensional stability
Custom machinability for seals, rings, vanes, bushings, and sleeves
Lightweight and adaptable in harsh environments
Typical Applications
Chemical and Petrochemical:
Heat exchangers, condensers, pump seals, reactor tanks
Withstands acids, alkalis, corrosive vapors
Metallurgy and Energy:
Electrolytic cells, continuous casting molds
Lubricant-free rotating equipment parts
Arcing components and electrodes
Industrial Equipment:
Compressors, injection molding machines, turbines
Conductive components for electronics and telecom
Emerging Fields:
New energy (fuel cells), aerospace, and defense sectors
High-temperature nuclear components and shielding
Related products
Select options
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page